VPN vs Proxy vs Smart DNS. Что такое VPN, Smart DNS и Прокси
- VPN vs Proxy vs Smart DNS. Что такое VPN, Smart DNS и Прокси
- Proxy vs DNS. What is a Smart DNS?
- Smart DNS Proxy servers. How Does a Smart DNS Work?
- Smart DNS vs VPN. What is VPN, Smart DNS, and Proxy
- DNS vs VPN speed. More of the popular arguments between VPN / DNS
- Proxy vs VPN Difference #1: What They Are and What They Do
- DNS VPN. Техническое: VPN и использование DNS
VPN vs Proxy vs Smart DNS. Что такое VPN, Smart DNS и Прокси
- VPN или виртуальная частная сеть в основном создает частную сеть , доступную через Интернет (общедоступная сеть). Это позволяет пользователям общаться так, как если бы они были напрямую подключены через частную сеть, когда они фактически общаются через Интернет. Сети VPN широко используются компаниями, которым необходимо разрешить удаленным сотрудникам доступ к частной сети , а также используются в качестве способа получения безопасного, зашифрованного доступа в Интернет.
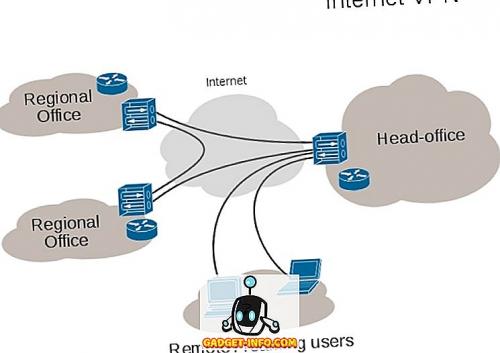
- Smart DNS - это сервер, который специально настроен для перенаправления пользователей на прокси-сервер. В отличие от VPN, которые перенаправляют весь интернет-трафик через свои туннели, Smart DNS перенаправляет только очень специфический трафик . Весь другой трафик может проходить через Интернет, как без Smart DNS, VPN или прокси-сервера. Таким образом, серверы SmartDNS в основном используются для доступа к веб-сайтам потокового вещания, которые ограничивают свое содержимое конкретными странами. В таких случаях сервер Smart DNS заставляет веб-сайт думать, что пользователь получает доступ к веб-сайту из подходящего местоположения.
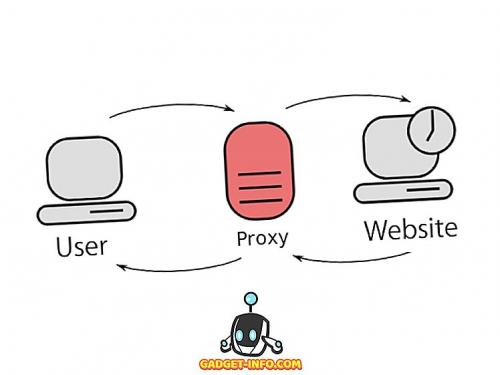
- Прокси-сервер, в основном, используется для поддержания анонимности в сети . Каждый отправленный вами веб-запрос сначала направляется на прокси-сервер, который затем передает его на сервер, для которого он был предназначен. Это заставляет сервер получателя думать, что Прокси-сервер отправил исходный запрос, поэтому пользователь остается анонимным. Когда сервер отвечает на прокси-сервер, он отправляет ответ обратно пользователю.
Proxy vs DNS. What is a Smart DNS?
A Smart DNS is a proxy service that enables you to unblock websites and get around location-based content restrictions. For example, if you’re in one place, but you want to watch a show available only in another country, a Smart DNS can get you there. Still with us? Good.
How does a Smart DNS work?
A Smart DNS works by connecting you to a proxy server located in the same country as the content you’re trying to reach. But first, what is DNS? Well, it stands for “domain name system,” and it’s your computer’s phone book for the internet. Just like you and the people you know (if any) have your own phone numbers, each website and online device has an IP address . It’s a string of numbers that identifies something, like a website or a computer, online.
The DNS pairs websites with their respective IP addresses. When you enter a website’s URL (like hidemyass.com ) into your browser, the DNS grabs the corresponding IP address and sends your request there. The DNS is what allows you to type in a website name rather than a string of numbers that would be pretty hard to remember.
A Smart DNS is “smart” because it knows when you need it to work, and when you don’t. When it detects that you’re attempting to visit a blocked site, your Smart DNS provider springs into action, redirecting your DNS to one of its proxy servers that can reach the site you want.
It won’t change your IP address (like a VPN will), but it will successfully reroute your traffic. That’s how you can use a Smart DNS to watch TV online.
Why use a Smart DNS?
The principal use of a Smart DNS service is to grant you access to location-locked content, most often for streaming TV shows and movies. It’s an increasingly popular solution for how to unblock websites.
Many subscription-based streaming services like Netflix offer a different selection of shows in various countries around the world, usually due to licensing restrictions. A Smart DNS service can grant you access to the content library in the country of your choice by delivering you that country’s version of the streaming service instead of your default one. While accessing your favorite content from abroad sounds great, there are also significant risks to consider.
What are the risks of using a Smart DNS?
Smart DNS proxies often cost money, and yet they can be pretty unreliable when it comes to unlocking all the content you want. And our crack team of sales experts have determined that people are unhappy when they don’t get what they paid for.
Another big problem is the risk of DNS hijacking . This is when a no-good hacker intercepts your connection and redirects you to a “spoofed” imitation of the site you want to use — one that can steal all your data. This can happen even when you’re not using a Smart DNS, but it’s way easier for hackers to pull off when you’re entrusting your connection to someone else entirely.
That’s why free DNS proxies are so dangerous: it’s like giving a stranger your wallet and PIN and asking them to use the ATM for you. If you’re interested in a Smart DNS, do your research first and choose a trustworthy premium service.
And don’t expect a Smart DNS to deliver any kind of anonymity.
A Smart DNS won’t hide your IP address or encrypt your connection, so if you’re looking to actually stay private online, this ain’t the way to do it. Smart DNS services simply aren’t designed to serve as privacy solutions.
Smart DNS Proxy servers. How Does a Smart DNS Work?
The Smart DNS server can be located anywhere in the world since the provider uses proxy servers in the country where the content you want to access is available to unblock websites. The new DNS you are provided with will essentially help you unblock websites in all the countries covered by the Smart DNS provider.
On top of that, a Smart DNS will also intercept your connection requests to the server you want to access, and replace any data in those requests that can leak your geo-location with new information that points to an “acceptable” geographical location.
So, for example, if you are located in Denmark, where BBC iPlayer is unavailable, a Smart DNS would help make it seem as if you’re accessing BBC iPlayer from the UK, giving you direct access to it.
Is Using a Smart DNS Legal?
Yes – using a Smart DNS is perfectly legal. After all, even Google offers access to free DNS server addresses for people who want to change their DNS address. Still, it’s worth mentioning that your ISP might interfere with you using a Smart DNS if they use a Transparent DNS Proxy. But even if that happens, it doesn’t mean that it’s illegal to use a Smart DNS.
Smart DNS vs. VPN – What’s the Difference?
Both a Smart DNS and a VPN (Virtual Private Network) are popular methods of bypassing geo-restrictions. The main difference is that a VPN helps you access blocked content by hiding your IP address , while a Smart DNS masks your original DNS address.
Other differences include the fact that:
- A VPN also encrypts your online traffic. As a result, your data is safe from hackers, and ISP and government surveillance, but your speeds might take a hit depending on how strong the encryption is.
- Since a VPN hides your real IP address, it helps you better mask your digital footprints. A Smart DNS can’t do that.
- A VPN can help you bypass firewalls at work or school that can prevent you from accessing the websites you want. On the other hand, a Smart DNS cannot bypass firewalls.
Overall, if you really care about getting the best online speeds while accessing geo-blocked content, you should use a Smart DNS. Otherwise, if you want toon top of accessing geo-restricted content, and also be able to bypass firewalls, you should use a VPN.
Does a Smart DNS Impact Your Internet Connection Speeds?
Not at all. Like we already mentioned, a Smart DNS – unlike a VPN – doesn’t use any type of encryption. As a result, you can use your original ISP-provided connection speed to enjoy any Internet content you want.
Smart DNS vs VPN. What is VPN, Smart DNS, and Proxy
- A VPN, or a Virtual Private Network basically creates a private network that is accessible over the Internet (public network). It allows users to communicate as if they were directly connected over the private network, when they are, in fact, communicating over the Internet. VPNs are widely used by companies that need to allow remote employees to access the private network , and are also used as a way to get secure, encrypted access to the Internet.
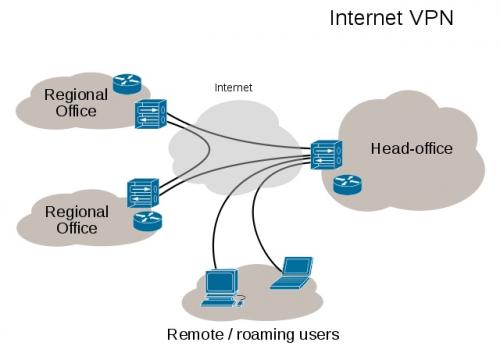
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
- Smart DNS is a server that is specially configured to redirect users to a proxy server. Unlike VPNs, which forward all internet traffic through their tunnels, Smart DNS only forwards very specific traffic . All other traffic is allowed to travel through the Internet as it would without a Smart DNS, VPN, or Proxy server. As such, SmartDNS servers are mostly used to access online streaming websites that restrict their content to specific countries. In such cases, the Smart DNS server tricks the website into thinking that the user is accessing the website from an eligible location.
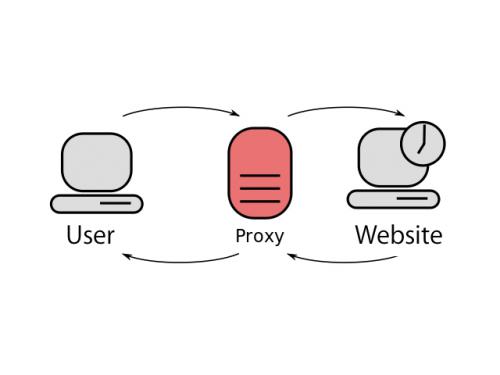
- A Proxy server, is basically used to maintain anonymity over a network . Every web request you send is first forwarded to the Proxy server, which then transmits it to the server it was intended for. This makes the recipient server think that the Proxy server sent the original request, therefore keeping the user anonymous. When the server responds to the Proxy, it sends the response back to the user.
DNS vs VPN speed. More of the popular arguments between VPN / DNS
So, Smart DNS is typically cheaper, but VPN gives you a lot more for your money. The big question is, do you need those extra services , or could you save yourself some cash?
When it comes to streaming media, we’d have to nudge towards Smart DNS, as it will do pretty much precisely what you need without the hefty charges.
- For bypassing Firewalls – VPN will do you proud; Smart DNS doesn’t stand a chance.
- Boosting security – VPN will completely block snoopers, hackers, trackers and more. Smart DNS won’t.
- Using torrent websites – VPN will switch your IP address and keep you anonymous. Smart DNS will show your true IP, leaving you extremely vulnerable.
- Highest network speeds – VPN uses part of your bandwidth to provide encryption; Smart DNS doesn’t do that so is generally faster.
- Available on most devices – Smart DNS can be applied to many devices where a VPN service or app isn’t available. However, Smart DNS is often far more complicated to set up than a VPN.
When it comes to applying your chosen service, VPNs tend to be a lot more user friendly. They’ll typically have a simple on/off button, and feature a kill switch for when you need one. Finding and changing your Apple TV DNS settings or understanding how to change the DNS server on LG smart TV, for example, can be both challenging and incredibly frustrating. Downloading VPN on your Mac, PC, mobile phone, or Smart TV, is pretty simple and straightforward.
Games consoles are another tricky option. Where many won’t have access to a native VPN app, digging into their DNS isn’t too straightforward either. Changing PS4 DNS settings or your Xbox 360 DNS can be far too taxing for the average gamer, so you’d have to search out an alternative, one that does the hard work for you. I mean, who needs to know the difference between primary and secondary DNS on your PS3 or where to find any model of PlayStation DNS settings, when all you really want to do is pull in a movie or a game that’s just been released in another country?
That’s where StreamLocator comes into its own.
StreamLocator works with your WiFi router, so you don’t need to worry about applying software and settings, or downloading apps to any of your devices.
Any device you connect to the Internet through our smart hub is automatically catered for. No more worrying about how you should switch your Xbox DNS settings, or what you need to have the correct DNS settings for UK Netflix, it’s all sorted for you. If you need to switch your Amazon Fire Stick DNS to access Prime Video in another country, we have an app for that, or our smart hub can do the job easily and simply, by itself.
Proxy vs VPN Difference #1: What They Are and What They Do
A proxy server is a computer system or router that acts as a relay between client and server on behalf of the user. Internet requests made by the user are routed to the proxy server first, evaluated, then forwarded to the internet. On the flip side, responses from the internet return to the proxy server before making their way to the user. The purpose of the proxy server is to mitigate threats to a network by guarding the identity of the resource server.
The most common types of proxies are:
SOCKS5 Proxies: Used for file sharing, video streaming services (e.g., Netflix), and gaming
HTTP Proxies: Used to access geo-restricted websites or in censored regions
Transparent Proxies: These proxies block certain sites in places (e.g., workplaces, schools) with public computers
A business-grade VPN provider enables:
- A secure connection to your company's virtual private network over the public internet
- A piece of layered security that protects company and personal data
- The ability to remotely access important network resources
- Connections between your branches and global locations
Two common types of business VPN setups are:
Remote Access : Hosted on the cloud or private network; connect users to a virtual private network from remote locations using VPN client apps installed on mobile devices
Site-to-Site : Connect two or more networks (e.g., a corporate network and a branch office network); intranet VPNs connect remote and main offices, extranet VPNs connect partners or customers with the main office network.
Key takeaway: A proxy passes web activity through a mediating server. A VPN works on an operating system level to secure all web traffic.
DNS VPN. Техническое: VPN и использование DNS
Спрашивают в комментариях к записке об использовании открытых и “чужих” сетей – зачем нужен собственный резолвер DNS, налаженный внутри VPN?
Давайте сперва вспомним типичный сценарий использования DNS. Для того, чтобы получить адрес узла, соответствующего данному имени, нужно опросить несколько серверов DNS. Обычно, этот опрос берёт на себя некий резолвер (специальная программа), принадлежащий провайдеру услуг доступа в Интернет и выполняющий извлечение адресов по запросам клиентских компьютеров.
Понятно, что в случае с собственным VPN-соединением, запущенным через “чужую” сеть, определять адреса серверов может всё тот же провайдерский резолвер. В конце концов, через VPN ходит TCP/IP, а не символьные имена доменов. После того, как резолвер определил IP-адрес сервера, соединение будет устанавливаться уже через VPN.
Но, как вы понимаете, паранойя встречается разных типов и масштабов, а резолвер провайдера как раз и используется для того, чтобы осуществлять подмену адресов страниц. Ведь именно при помощи подстановки “кривого” адреса в ответ на запрос о любом домене происходит переадресация браузера на замечательные страницы с предложением приобрести ту или иную услугу, с напоминанием о том, что на счёте мало денег, и так далее, и тому подобное. “Чужой” резолвер ставит крест на всех полезностях VPN, если, конечно, вы планируете использовать DNS. (Кроме того, если вы настроили локальную маршрутизацию таким образом, что весь трафик ходит через VPN, может возникнуть проблема: резолвер владельца сети не станет обслуживать запросы, поступающие с вашего компьютера, потому что они будут приходить извне – со стороны шлюза VPN.)
Другое решение – держать рекурсивный резолвер локально, на своём ноутбуке. Я не уверен, может ли это делать Windows (наверное, может), но с юниксоподобными системами проблем нет, достаточно поднять локальный BIND. Трафик резолвера нужно завернуть в VPN, это обеспечит секретность. (Тут есть подводный камень: использование NAT, – а трафик из VPN во внешний мир может выходить именно через NAT, – грозит тем, что испортится один из защитных механизмов DNS, который называется “рандомизация портов UPD на источнике запроса”; но это другая история.) А главный недостаток один: нужно на каждом клиенте VPN держать свой рекурсивный резолвер. Неудобно. Поэтому куда более логично разместить собственный резловер на сервере, обеспечивающем VPN. Всё равно этот сервер работает постоянно.
А кроме того, редкий провайдерский резолвер поддерживает DNSSEC. Я таких вообще не видел.